Four properties of gases determine the physical behaviour of gases:
- The amount of gas (in moles)
- Volume
- Temperature
- Pressure of Gas
Pressure is defined as a force per unit area or in other words, a force divided by the area over which the force is distributed. The SI unit for force is a newton which is equivalent to 1N= 1 kg m s-2. Therefore, the unit for pressure is N/m2. A pressure of one newton per square metre is define as one Pascal.
LIQUID PRESSURE
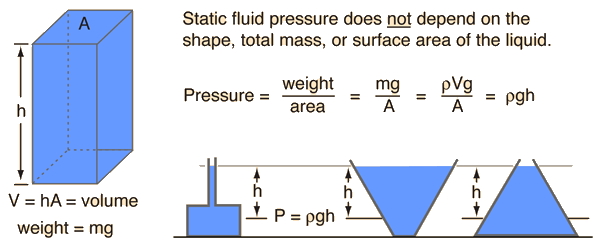
The pressure of a gas usually measured indirectly by comparing it with the liquid pressure. The pressure of a liquid depends on the height of the liquid and the density of the liquid.
Thus g is a constant, liquid pressure is directly proportional to the liquid density and the height of the liquid column.
BAROMETRIC PRESSURE
In 1643, a device called a barometer was invented to measure the pressure exerted by the atmosphere.
SO HOW DID IT WORK? Good question. Evangelista Torricelli who constructed the barometer used two tubes: an open-end tube and a closed-end tube and filled the entire tubes with mercury and placed it in a basin filled with mercury. WHAT HAPPENED? The open-end tube was placed upright in the basin and was noticed that the mercury levels inside and outside the tube were the same. In the closed-end tube, which was inverted and quickly placed into the basin, its mercury levels had fallen to certain height and remained there. WHY? Torricelli noted:
- In the open-end tube, the atmosphere exerts the same pressure on the surface of the mercury both inside and outside of the tube
- Inside the closed-end tube, there is no air above the mercury (a vacuum) and the atmosphere exerts a force on the surface of the mercury outside the container. This force is transmitted through the liquid, holding the mercury column within the tube. The column exerts a downward pressure that depends on the height and density of the mercury.
When the pressure at the bottom of the mercury column = pressure of the atmosphere, the column height is maintained. The height of the column gives a measure of barometric pressure and is expressed as a unit of mmHg (millimeter of mercury).
CONVERSIONS
The SI unit for pressure is defined as one standard atmosphere (atm). BUT WAIT HOW DO I CONVERT FROM mmHg TO atm? Good question. Although you will mostly likely convert from mmHg to atm, there are chances that you will have to convert other units. Why not give you them all? But based on your question:
1 atm= 760 Torr = 760 mmHg
MANOMETERS
Though barometers are highly useful tools for measuring pressure, it is rarely used to measure other gas pressures. However, the pressure of the gas to be measured can be compared with barometric pressure by using a manometer.
HOW DOES IT WORK?
When the gas pressure being measured and the prevailing atmospheric (barometric) pressure are equal, the heights of the columns in the two arms of the manometer are equal. If there is a difference in height in the two arms, it signifies a difference between the gas pressure and the barometric pressure.
To view sample problems and solutions, click on the next page titled "Chem 1000- Gases, an intro- Sample problems and solutions"



No comments:
Post a Comment