Robert Boyle discovered the first simple law, which was named Boyle's Law which states:
For a fixed amount of gas at a constant temperature, the gas volume is inversely proportional to the gas pressure
- If pressure increases, volume decreases
- If pressure decreases, volume increases
CHARLES'S LAW
Jacques Charles discovered the relationship between temperature and volume in which was later described as Charles' Law. It states:
The volume of a fixed amount of gas at a constant pressure is directly proportional to the Kelvin (absolute temperature)
Based on the diagram above, Charles' Law states that the volume of the gas is directly proportional to the temperature if pressure is constant. That is,
- If temperature increases, volume increases
- If temperature decreases, volume decreases
Charles' Law can be summed up with the following equation:
Note that the absolute zero of temperature is the temperature at which the volume of a hypothetical gas is zero. This is -273.15 C or 0 K. The relationship between Celsius and Kelvin can be explained through the equation:
where T is in K and Tc is in Celsius
STANDARD CONDITIONS OF TEMPERATURE & PRESSURE
Now that you learned some of gas properties, you can tell me that gas properties depend on temperature and pressure. However, there needs to standard conditions of temperature and pressure so that different gases can be compared to. Standard conditions of temperature and pressure or more commonly known as STP is the following:
- Standard Temperature= 0 C or 273.15 K
- Standard Pressure= 1 bar= 10^5 Pa
AVOGADRO'S LAW
Amedeo Avogadro proposed the "equal volumes-equal numbers" hypothesis which he stated that equal volumes of different gases compared at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of molecules and vice versa. This can be summed to what is known as Avogadro's Law:
At a fixed temperature and pressure, the volume of the gas in directly proportional to the amount of gas
- If number of moles of gas increases, the volume increases
- If number of moles of gas decreases, the volume decreases
Note that V/n is equivalent to molar volume. Molar volumes vary at different temperatures and pressure but is equal to certain values:
- Molar volume at 0 C and 1 atm = 22.414 L/mol
- Molar volume at STP = 22.711 L/mol
WAIT BUT WHAT IF PRESSURE, TEMPERATURE OR AMOUNT OF GAS IS NOT CONSTANT, THEN WHAT DO I DO?
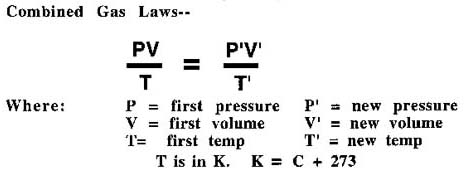
Good question. Remember, to use Boyle's Law, temperature must be constant.Charles' Law, Pressure must be constant and for Avogadro's Law, pressure and temperature must be constant. SO WHAT IF IT ISN'T? This is where we combine all the simple laws:
This is known as Combining Gas Law
Be sure to click on the following page " Chem 1000- Simple Gas Laws Problems & Solutions" to extra practice on these laws






No comments:
Post a Comment